HOW TO WRITE THE BEST BUSINESS PLAN IN 2024
Find below our top and best tips, steps and instructions for writing the best business plan and template in 2024.
Brought to you by Mau, Global Head of Business Strategy at eDigital.
WHAT IS A BUSINESS PLAN?
The best definition of a business plan is a written document that details your proposed venture. There’s no such thing as an “official” business plan, but the idea highlights the misuse.
Some people spend months developing a “business plan” instead of developing their businesses.
A winning business plan is a road map (Not the result) of one of the key activities of your business: business planning.
Business planning is a process that allows you to revise and review your overarching business strategy, a tool for managing and steering a “real” business.
The process of business planning and writing your business plan involves looking at where you want your company to be in the next 1 to 3 years and determining what you need to do to get there.
A well-defined business plan must describe:
- The nature of your business: why you are in business.
- Few specific business goals and objectives: How you are going to make a profit and increase brand equity.
- The key customer segments (most profitable customer clusters) you are going to target and serve.
- The specific customers’ needs you are going to solve really well. We call this part the unique selling proposition (USP)
- The resources, tools and insights you will need to effectively run your business.
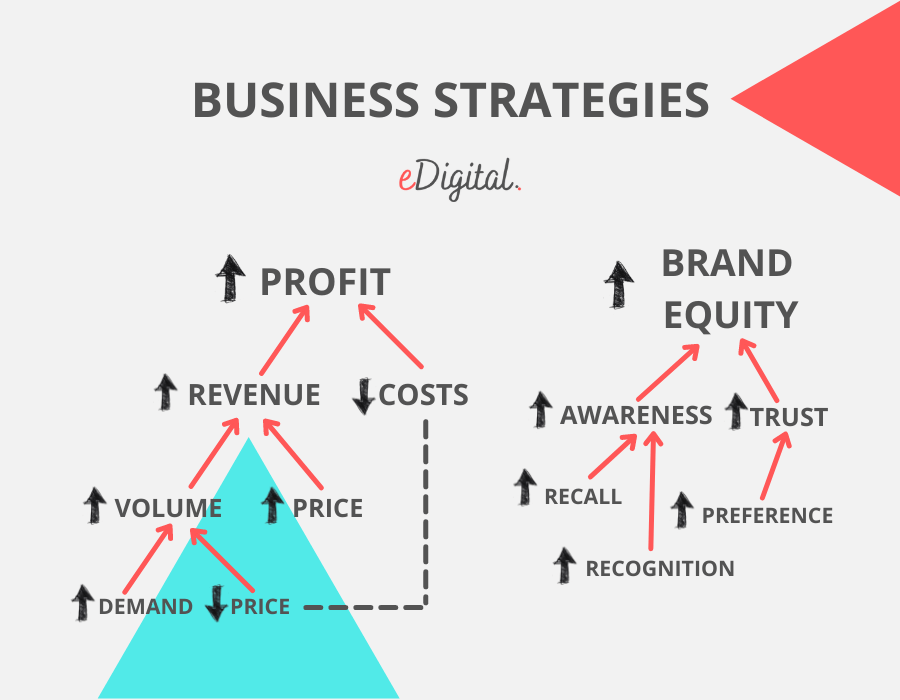
Below is a chart that shows you how your business can make a lot of money.
Exciting, right?
Well, as you can probably guess, there’s a catch.
If you want to increase your profits, there are only two ways to do it: lower your costs or increase your revenue.
If you want to increase your revenue, you can either increase your price or increase your volume. What’s volume? Depending on the type of business, volume can mean units sold, capacity, leads, or something else.
Notice how each outcome is impacted by other decisions in the visualisation below.
BUSINESS STRATEGIES MUST BE INCLUDED IN A BUSINESS PLAN
Margin, revenue, volume and reducing costs are key elements most businesses think about in their financials Which one works best for your business plan?
- Improve margin or profit: This is great for companies looking to reduce costs and increase revenue. There’s usually a trade-off, though. For example, some investments to reduce costs may not pay for a few years, making the company less money in the short term, even though it’ll be very profitable in the long term. Typically, established companies or those with smaller profit margins, like retail companies, prioritise this.
- Grow revenue: Companies often grow their revenue by either trying to increase the total number of sales at the same price or increasing the price — that is, revenue could go up, even if total sales don’t.
- Increase volume: Companies who wish to increase volume will either decrease prices to drive more sales or use various tactics to drive more demand. However, this might mean being less profitable in the short term.
DEFINING STRATEGIC OBJECTIVES IN YOUR BUSINESS PLAN
Many executives also use strategic objectives when crafting a professional business plan, outlining how they’ll achieve their financial objectives. An example of a strategic objective is increasing your brand equity.
What do I mean by brand? A brand means how people think about your company and products. That’s your brand.
Brand equity (also called brand strength) describes the value of having a well-known name (like Google). The idea is that a well-known brand name can generate more revenue simply from brand recognition.
It’s difficult to acquire new customers if consumers aren’t aware of your brand or don’t have a favourable (preference) opinion of it. This also makes it challenging to keep existing customers. Therefore, brand equity is really important for the company’s ability to grow sales in the long term. This brings us to long-term vs. short-term thinking.
SHORT-TERM VS LONG-TERM THINKING
In order for your business to prosper, you’ll need to be able to make money today, as well as in the future. You need to balance your short-term and long-term goals in your business plan.
An example
Because of an increase in the price of raw materials, an electronics company chooses to reduce their investment in advertising instead of increasing its prices. The choice isn’t easy. Increasing prices could mean losing current customers who are price-sensitive or less loyal. Reducing investment in advertising reduces the company’s ability to attract new customers, which can result in a decrease in long-term sales.
Remember: Every short-term decision needs to work toward achieving a long-term goal as well.
GROWTH TARGETS
What’s a reasonable growth target to be added to your business plan? How should you go about setting your business growth targets?
This depends predominantly on your brand’s maturity in the market you compete in.
If you’re a mature company, growth is likely to be modest, as there is increasingly less room for you to grow. This isn’t necessarily bad. Low single-digit growth for a large brand may translate into more dollars than double-digit growth for a small brand.
On the other hand, a less-established company could reasonably aim for more ambitious growth. Just be mindful of diminishing returns, and understand how far you can push your growth ambitions.
When deciding which return on investment (ROI) target to aim for, a higher ROI may not always be the best choice. In order to achieve your growth targets, you may choose to invest profit margin into faster customer growth.
For example, if a $2 ROI offers twice the customer growth as a $3 ROI, your business may choose $2 as a target, although this is the second-best option for profitability.
Sometimes the right target is the one that keeps your company in business. That could be fine only if you are in playing on tough economic, competitive, social or political conditions.
YOUR BUSINESS PLAN IS A ROADMAP
Your business plan is your roadmap on how to create a successful and profitable business.
In its essence, a business plan is simply proof that you have thought through all of your business options, you have planned for business and market contingencies and you feel confident that you have a plan that will help your business be successful.
Writing the best business plan also means crafting a roadmap to help you keep your business moving in the right direction.
It is a beneficial exercise for business owners who are just starting out and for those who need to make changes to their business operations.
“Some people get bored or scared with the idea of writing a business plan. You can start with your simple ideas: This is the exact problem I want to solve for this exact type of person, this is why people will buy it, this is what I think it will cost to deliver it, these are the resources, talent and money needed to make it work, this is what I will do if I do not sell as much, etc. The larger the business, the more formal the plan. Also, if you need equity financing, you will need to have a business plan ready to present to potential investors”
Mau. – Global Head of Business Strategy at eDigital
A company’s business plan is a living document and needs to be updated at least once a year.
A successful business plan should be used:
- By managers and executives for internal planning.
- As the basis for loan applications from banks and other lenders.
- To persuade investors that a company is a good investment.
- As a road map to the future helping entrepreneurs and business owners think through their strategies, evaluate their basic business concepts, recognize their business’s limitations, and avoid a variety of mistakes.
BUSINESS PLAN STRATEGIC PLANNING
Strategic planning is a business process to produce innovative and creative business ideas that serve as the core framework for the company and designing its future. Your business plan should be part of your company’s strategic planning.
Strategic planning will help you look into the sideways threads. It’s the sideways threats that kill companies, If you think of Kodak and Fuji, competing in the film industry for 100 years, but then ultimately it turns out to be Instagram. Netflix is the result of a sideway thread Blockbuster did not review in due time. The famous Amazon Flywheel business model continues to be the key driver for business success.
THE TOP 7 REASONS FOR WRITING A BUSINESS PLAN
It’s tempting to start executing business activities when you’re excited about a new business, but taking the time to write the best business plan and get your business ideas and strategies on paper allows you to complete a number of beneficial actions:
- Evaluate your key business idea. A business plan can make an idea more tangible, helping you see if it is truly viable. If you’ve got multiple ideas in mind, a rough business plan for each can help you focus your time and energy on the ones with the highest chance of success.
- Fully profile and understand your ideal customers and close competitors. To write a business plan, you’ll need to research your ideal customer (most valuable customers) and your competitors—information that will help you make more strategic decisions.
- Strategic planning. Whether your goal is to start a new business or scale an existing business to the next level, a business plan can help you clarify your ideas, understand your business scope, understand the amount of time, the type of resources, the quantity of money and resources you will need to get started and list the activities to be completed and identify gaps and “unknowns” to address.
- Have your strategies, goals and tactics clear. Writing a business plan can show you the actionable next steps to take on a big, abstract idea. It can also help you narrow down your strategy and identify clear-cut tactics that will support it.
- Scoping. If you do not have a business plan, cost overruns and delays are all but certain. A business plan helps you see the full scope of work to be done and adjust your investment of time and money accordingly.
- Secure talent and /or strategic partnerships. When you need buy-in from potential employees and partners, especially in the early stages of your business, a clearly written business plan is one of the best tools at your disposal. A business plan provides a refined look at your goals for the business, letting partners judge for themselves whether or not they agree with your vision.
- Secure funds. Securing funding for your business, whether from investors or a bank, is one of the most common reasons to create a business plan.
WHY USE A BUSINESS PLAN TEMPLATE?
Below are the top key benefits of writing a successful business plan from an existing outline or template.
- No blank-page paralysis. A blank page can be intimidating to even the most seasoned business strategists or entrepreneurs. Using an established business framework and guidelines can help you get past the inertia of starting your business plan, and it allows you to skip the work of building an outline from scratch. You can always adjust a template to suit your needs.
- Guidance on what to include in each section. If you’ve never sat through a business class, you might never have created a SWOT analysis or a balance sheet before. Templates that offer guidance—in plain language—about how to fill in each section can help you navigate sometimes-daunting business jargon and create a complete and effective plan.
- Knowing you’ve considered every section. In some cases, you may not need to complete every section of a business plan template, but its initial structure shows you you’re choosing to omit a section as opposed to forgetting to include it in the first place.

I did not know how to draft a business plan and this template was really useful and saved me tons of time. Thank you.
Jack M. 
HOW TO WRITE A THE BUSINESS PLAN IN 2024
Writing the best business plan is an essential tool for building and growing a successful business or new startup venture. A well-written business plan will define the direction of your business, create strategies to achieve your goals and help you win finance from top investors or venture capital firms.
This premium Business Plan template – carefully crafted by Mau, Global Head of Strategy at eDigital – steps you through the process of how to create a professional, solid, well-structured business plan tailored to your current company needs.
BUSINESS PLAN WRITING ESSENTIALS
Before you use this exclusive Business Plan Template, consider the following:
- Do your research. You will need to make quite a few decisions about your business including structure, marketing strategies and finances before you can complete the template. By having the right information to hand you also can be more accurate in your forecasts and analysis.
- Determine who the plan is for. Does it have more than one purpose? Would it be used internally or will third parties be involved? Deciding the purpose of the plan can help you target your answers. If third parties are involved, what are they interested in? However, don’t assume they are just interested in the finance part of your business. They will be looking for the whole package.
- Do not attempt to fill in the template from start to finish. First, decide which sections are relevant to your business and set aside the sections that don’t apply. You can always go back to the other sections later.
- Read our tips added in [italicised text]. The italicised text is there to help guide you by providing some more detailed questions you may like to answer when preparing your response.
- Get support. If you aren’t confident in completing the plan yourself, you can enlist the help of a professional (i.e. Single Business Service, Business Enterprise Centre, business adviser, or accountant) to look through your plan and provide you with advice.
- Actual vs. expected figures. Existing businesses can include actual figures in the plan, but if your business is just starting out and you are using expected figures for turnover and finances you will need to clearly show that these are expected figures or estimates.
- Write your summary last. Use as few words as possible. You want to get to the point but not overlook important facts. This is also your opportunity to sell yourself. But don’t overdo it. You want prospective banks, investors, partners or wholesalers to be able to quickly read your plan, find it realistic and be motivated by what they read.
- Proofread. Your business plan is there to make a good impression. Errors will only detract from your professional image. So ask a number of impartial people to proofread your final plan.
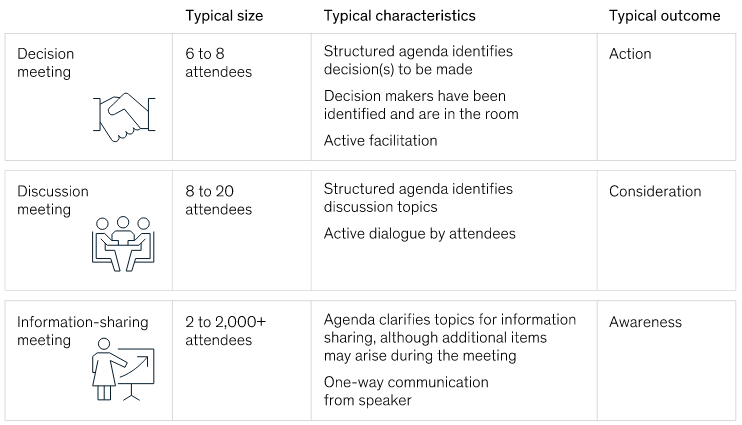
- Effective stakeholder consultation is important. Involve all key stakeholders who deal with your company’s strategic vision. If a set of meetings are required to define your digital business plan with different stakeholders; ensure you have a structured agenda and expected outcomes so the business plan is agreed /approved. The below goal /outcome matrix will help you have an effective meeting.
goal outcome matrix meeting work productivity
STRUCTURE FOR A WINNING BUSINESS PLAN
Below is an example of the traditional business plan structure.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
This is usually a 2-3 page summary of the entire business plan. It is a very important part of the plan, in that it is designed for key people you need support from and who do not have the time to read your whole plan. It usually summarizes your business model’s competitive advantages, sales and profit projections, financial requirements, plans to repay lenders or investors, and the amount of financing requested.
“Business plans are a valuable, iterative, document that can serve as a successful benchmarking tool. Where did your business exceed expectations? In what areas did your strategy maybe fall short? While it’s fine to “pivot” your company based on what you’ve seen in the market, having something in writing puts the responsibility on you to be honest about your company’s performance”
Kim L – International Business Strategist.
BUSINESS DESCRIPTION
The business description includes not only a profile of the company but also a picture of the industry in which the company operates. Every business operates within a specific context that affects its growth potential. The description of a company’s operating environment may cover new products and developments in the industry, trends and outlook for the industry, and overall economic trends. It also lists the unique features that give the company an edge in the environment in which it competes. A brief company history reveals how specific products and services were developed, while descriptions of pertinent contracts and agreements should also be mentioned (information on contracts and legal agreements may also be included in an appendix to the business plan).
- General description of the business
- Industry background
- Goals
- The potential of the business
- Milestones
- The uniqueness of your product or service: here you differentiate your company’s products or services from those of the competition. It describes specific customer needs that are uniquely met by the firm’s products or services. Product features are translated into customer benefits. Product life cycles and their effects on sales and marketing can be described.
- Research and Development: The company’s plans for a new generation of products or services are included in this section.
“The biggest reason to write out a business plan regardless of any financing option concerns is that it can help you stay organized and remain on track. Businesses without a plan can easily get off-target, and revenues will suffer as a result. Creating a plan with expense projections, revenue forecasts, and more can help a small business remain committed to its long-term goals.”
Chris M – CEO
MANAGEMENT
The quality of a company’s management team can be the most important aspect of a business plan. This section presents the strengths of the company’s management team by highlighting relevant experience, achievements, and past performance. Key areas include management’s ability to provide planning, organizational skills, and leadership. This section also contains information about the company’s ownership and workforce. It may present an existing or planned organisational structure that will accomplish the goals set forth in the business plan. Specific management and control systems are often described as well.
- Management team (key personnel)
- Legal structures: tock agreements, employment agreements, ownership
- Board of directors, advisors, consultants
MARKETING STRATEGY
- Research and analysis
- Target market (customers) identified. A customer analysis provides a picture of who buys and uses the company’s products or services.
- Market size and trends: A thorough market analysis serves as the basis for a company’s sales and marketing plans. The analysis generally covers the company’s competition, customers, products, and market acceptance. This section of the business plan highlights how the company’s products or services satisfy previously unfulfilled market needs. It also includes evidence of market acceptance of the company’s unique products or services.
- Competition: The competitive analysis details the competition’s strengths and weaknesses, providing a basis for discovering market opportunities.
- Estimated market share
- Marketing plan: The marketing plan delineates the methods and activities that will be employed to reach the company’s revenue goals. This section describes the company’s marketing and sales programs. The latter is supported by conclusions drawn from the market analysis. Different revenue outcomes may be presented to allow for contingency planning in the areas of finance and production.
- Market strategy – sales and distribution
- Pricing
- Advertising and promotions. it is important to have your advertising and sales promotions calendar ready.
“Business planning is incredibly helpful for describing what you do, understanding who your competitors are, and crafting a realistic plan. Each of these activities is crucial if you are looking to launch or expand a venture, and learning to speak concisely about your company will always be crucial no matter what stage you’re in”
Paige – Marketing Growth Director
OPERATIONS AND LOGISTICS
- Identify location
- Advantages
- Zoning
- Taxes
- Proximity to supplies
- Access to transportation
Logistics and operations are the workflows you’ll implement to make your ideas a reality. If you’re writing a business plan for your own planning purposes, this is still an important section to consider, even though you might not need to include the same level of detail as if you were seeking investment.
Cover all parts of your planned operations, including:
- Suppliers. Where do you get the raw materials you need for production, or where are your products produced?
- Production. How long does it take to produce your products and get them shipped to you? How will you handle a busy season or an unexpected spike in demand?
- Facilities. Where will you and any team members work? Do you plan to have physical retail space? If yes, where?
- Equipment. What tools and technology do you require to be up and running? This includes everything from computers to lightbulbs and everything in between.
- Shipping and fulfilment. Will you be handling all the fulfilment tasks in-house, or will you use a third-party partner?
- Inventory. How much will you keep on hand, and where will it be stored? How will you ship it to partners if required, and how will you keep track of inventory?
FINANCIAL
This section covers the financing and cash flow requirements implicit in other areas of the business plan. It contains projections of income, expenses, and cash flow, as well as descriptions of budgeting and financial controls. Financial projections must be supported by verifiable facts, such as sales figures or market research. Monthly figures are generally given for the first two years, followed by annual figures for the next three years. If the business plan is written for investors or lenders, the amount of financing required may be included here.
- Financial forecast
- Profit and loss
- Cash flow
- Break-even analysis
- Cost controls
- Budgeting plans
“A lot of ideas sound great on paper and even in discussions. However, simple math can make or break an idea. Before we launch any new idea, we at least create a financial model to project the ROI from several realistic scenarios. You can save a lot of time and frustration thinking through the numbers, and making sure it’s possible to hit your revenue and profit goals.”
Lauren W – Managing Director
Income statement
Your income statement is designed to give readers a look at your revenue sources and expenses over a given time period. With those two pieces of information, they can see the all-important bottom line, or the profit or loss your business experienced during that time. If you haven’t launched your business yet, you can put together a forecast of the same information.
Balance sheet
Your balance sheet offers a look at how much equity you have in your business. On one side, you list all your business assets (what you own) and, on the other side, all your liabilities (what you owe). This provides a snapshot of your business’s shareholder equity, which is calculated as assets – liabilities = equity.
Cash-flow statement
Your cash-flow statement is similar to your income statement, with one important difference: it takes into account when revenues are collected and when expenses are paid.
When the cash you have coming in is greater than the cash you have going out, your cash flow is positive. When the opposite scenario is true, your cash flow is negative. Ideally, your cash-flow statement will help you see when cash is low, when you might have a surplus, and where you might need to have a contingency plan to access funding to keep your business solvent.
It can be especially helpful to forecast your cash-flow statement to identify gaps or negative cash flow and adjust operations as required.
CRITICAL RISKS
This section defines problems and challenges that the company may face and outlines contingency plans for overcoming obstacles that might arise. Specific topics that may be explored are competitive responses, areas of weakness or vulnerability, legal constraints, staffing, and continuity of leadership.
- Obstacles and risks
- Alternative courses of action
“Although it took several weeks and I’ve barely looked at it since, I credit my business plan for helping me understand a brand-new industry in an extremely deep way before actually entering it, and for forcing me to deeply examine how we would fit into the market and what TalentEgg’s probability of success was. As a “risk averse” entrepreneur, it was critical ”
Jason T – Entrepreneur
HARVEST STRATEGY
- Transfer of assets
- Continuity of business strategy
- Identify successor
MILESTONE SCHEDULE
- Timing and objectives
- Deadlines and milestones
- Relationship of events
APPENDIX
An appendix may include a variety of documentation that supports different sections of the business plan. Among the items that may be found in an appendix are footnotes from the main plan, biographies, graphs and charts, copies of contracts and agreements, and references.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Citing your sources is critical to establishing your credibility and for remembering how you arrived at the conclusions and figures you present in your business plan.
AN ALTERNATIVE BUSINESS PLAN MODEL
Traditional business plans are often misused to obfuscate, bore and show an ability to comply with expectations. If you want the real truth about a specific business and where it’s going, you would rather see something else.
You will divide the modern business plan into five simple sections:
TRUTH
Truth can take as long as you need to tell it. It can include spreadsheets, market share analysis and anything needed to explain to someone about your market works, the needs that already exist, the competitors in your space, technology standards and the way others have succeeded and failed in the past. The more specific the better. The more ground knowledge the better. The more visceral the stories, the better. The point of this section is to be sure that you’re clear about the way you see the world, and that you, your team, investors and lenders agree on your assumptions. This section isn’t partisan, it takes no positions, it just states how things are.
ASSERTIONS
The assertions section is your chance to describe how you’re going to change things. We will do X, and then Y will happen. We will build Z with this much money in this much time. We will present Q to the market and the market will respond by taking this action. This is the heart of the modern business plan. The only reason to launch a project is to change something, and I want to know what you’re going to do and what impact it’s going to have. Of course, this section will be incorrect. You will make assertions that won’t pan out. You’ll miss budgets and deadlines and sales; that’s fine! In the next section, you will provide solutions if your assertions do not happen.
ALTERNATIVES
If your assertions don’t pan out, is it over? In this section, you provide alternatives if your assertions do not happen. How much flexibility does your product or team have? What resources you will have available to flex your business if needed?
PEOPLE
The people section rightly highlights the key element: who is on your team and who is going to join your team. This does not mean providing resumes, this means describing their attitudes and abilities and track records in shipping and delivery.
MONEY
This last section is all about money. How much do you need, how will you spend it, what does cash flow look like, P&Ls, balance sheets, margins and exit strategies?
Note: Your local venture capitalist might not like this format, but it will help your team think through the hard issues more clearly.

The template was a perfect addition to my business. Its flexible taxonomy allows for easy customisation. Thank you.
Ella J. 
THE TOP BENEFITS OF HAVING YOUR BUSINESS PLAN READY
Designing, agreeing and actioning your business plan can have an immediate influence on your company’s success. How to write a business plan is one of the most important skills if you want to be a successful serial entrepreneur or looking for serious venture capital or investment. Having your business proposal ready to be examined by key parties or board members will offer you the benefits of:
- Forces you to summarise the business model. As you will have limited resources, time and budgets, you will need to be clear about what business model you will be using to profit from your venture. There might be many ways your business can make revenue but not all might be strategic for you and optimise your resources.
- Prioritising budgets and hiring decisions. Once you are clear on your business model, it will be easier for you to know where your budget allocations need to be and what exact hiring decisions you need to make to support your business model.
- Makes your vision a reality. Your business plan becomes a key plan for the company with clear goals and objectives. Your business plan should allow you to foresee changing market conditions as much as possible.
- Establish direction. Clearly defines your company’s purpose and establishes realistic goals and objectives consistent with the mission which can be clearly communicated to constituents. Your business plan should provide a base from which progress can be measured, employees compensated and boundaries established for effective decision-making.
- Provides agreement. Your business plan communicates to others the scope and nature of your business strategy. A clear road map helps you develop consensus and support to ensure agreed commitment.
- Prepares the owner or entrepreneur. The entire business planning process forces the entrepreneur to view the venture critically and objectively; analyse all aspects of the venture and prepare an effective strategy to deal with the uncertainties that arise. The competitive, economic, financial and SWOT analysis included in the business plan subject the entrepreneur to close scrutiny of his or her assumptions about the venture’s success and provide a path to polish the market entry strategy.
- Provides measurable benchmarks. A business plan quantifies objectives for comparing forecasts with actual results.
- An effective communication tool. A well-structured business plan provides the entrepreneur with a communication tool for outside financial sources as well as an operational tool for guiding the venture towards success.
- Market potential clarity. Details of the market potential and plans for securing a share of that market.
- Confirms your business’s financial health. The venture’s ability to service debt or provide an adequate return on equity. The business plan also identifies critical risks and crucial events with a discussion of contingency plans. Your business plan will be super helpful when seeking the allocation of funds and assets for international business or seeking financial assistance from lenders and/or investors.
- Helps you allocate responsibilities. Allocates responsibilities and provides baselines and metrics for an evaluation of results.
- A business plan confirms your USP. Your business plan must have clearly marked the unique value (unique selling proposition) you bring to the market and how your best practices are going to be different from your competitors’ ones. Avoiding this way, competitive convergence.
- Confirms meaning and purpose to employees. Your business plan confirms the reason why you are in business and the passion and motivation you and your team members have to make your customers fully satisfied with your offering.
- Guides your growth targets. Whether is to increase profitability, market share or brand equity, the best business plan should uncover the customer segments, market conditions, and product and service offerings that are in the best interest of the company. Your business plan should have an intent and targeted approach to markets and opportunities which guide your sales and marketing efforts, distribution and other business decisions which ultimately mean more profit to the bottom line and a stronger market position.
- Helps you reduce risks. Another reason for entrepreneurs to make a business plan a priority is that it helps them reduce risk, particularly in periods of economic uncertainty. As part of the process of writing a business plan, you’ll be assessing your current situation, resources, strengths and weaknesses, competitors and the business environment. This way, you will be better equipped to make decisions and therefore minimise risk.
- Helps you manage your cash flow. Careful management of cash flow is a fundamental requirement for all businesses. The reason is quite simple–many businesses fail, not because they are unprofitable, but because they ultimately become insolvent (i.e., are unable to pay their debts as they fall due). While the break-even point–where total revenue equals total costs–is a highly important figure for start-ups, once a business is up and running profitably, it becomes less important. Cash flow management then becomes more vital when businesses pursue investment opportunities where there are significant cash outflows, in advance of the cash flows coming in. These opportunities need to be assessed against any seasonal variations in the business and the timing of the flows. If you are a “cash-only” business, you can bank the income immediately; however, if you sell on credit, you receive the cash in the future and hence may need to pay some of your own expenses before that income hits your account. This will put a further strain on the company’s solvency and hence a well-structured business plan will help you manage funding requirements in advance.
- Creates motivation. One of the first steps you should take when writing your business plan is to create a vision of where you would like to be five to ten years in the future. Creating this Vision becomes motivational because it allows you to see the possibilities you can create for your business. For example, if you know that your goal is to take your business international, you will be cognizant of the steps necessary to get there. You will focus on developing international relationships, learning the customs of other countries, and brushing up on the language.
- Support your strategic exit. Finally, at some point, your company will decide it is time to exit. Considering the likely exit strategy in advance can help inform and direct present-day decisions. The aim is to liquidate the investment, so the owner/current investors have the option of cashing out when they want. Common exit strategies include Initial Public Offering of stock (IPOs), Acquisition by competitors, mergers, family succession and management buy-outs.
PITFALLS TO AVOID WHEN WRITING YOUR BUSINESS PLAN
- Pitfall 1: No realistic goals
- Pitfall 2: Failure to anticipate roadblocks
- Pitfall 3: No commitment or dedication
- Pitfall 4: Lack of demonstrated experience (business or technical)
- Pitfall 5: No market niche (most profitable customer segment)
- Pitfall 6: Not offering demonstrable solutions to all parties: Entrepreneurs, market (user), investors.
- Pitfall 7: Letting others decide on the final version. If consultants are sought to help prepare a business plan, the entrepreneur must remain the driving force behind the plan. Seeking the advice and assistance of outside professionals is always wise. You – as the business owner – are responsible for every aspect of the business plan, since it is you who come under the scrutiny of financial sources.
WHO WILL BE LIKELY TO READ YOUR BUSINESS PLAN
- Venture capitalists and investors
- Bankers
- Investors
- Potential customers
- Lawyers
- Consultants
- Suppliers
THINK ABOUT YOUR BUSINESS PLAN READERS
The reality is most of the readers of your business plan will not really read all the words. They will scan your plan – the five minutes read – to find out:
- The characteristics of the venture and its industry
- The financial structure of the plan (amount of debt or equity investment required)
- The latest balance sheet (to determine liquidity, net worth, and debt/equity)
- The quality of entrepreneurs in the venture (sometimes the most important area of your plan)
- The unique feature of this venture (find out what is different)
WHAT FORMAT TO CHOOSE FOR YOUR BUSINESS PLAN?
Writing a winning business plan might require having different samples in different formats (if time allows) as it can help you decide the best format you want to choose. If you lack time, a Business Plan sample in Google Docs, Microsoft Word or PDF formats is the most common execution. Other entrepreneurs select PowerPoint templates (PPT). Deciding how to make your business plan is your final decision but it is always best practice to check who the most important people – who want to read it – are and how they would like it to be delivered (what format). As with any business proposal format, it needs to keep professional and free of errors or mistakes.
BUSINESS PLAN GUIDELINES TO REMEMBER
- Keep the business plan or business proposal respectably short
- Organise and package the plan appropriately
- Orient the plan toward the future
- Avoid exaggeration
- Highlight critical risks
- Give evidence of your effective and successful entrepreneurial team
- Do not over-diversify (keep the focus on the unique feature that will be your key differentiator in the next 1-2 years)
- Identify the target market – your key most valuable customer segment
- Keep the plan written in the third person
- Capture the reader’s interest by using visuals when necessary
- Even if you are a small business owner (restaurant, others) be clear on what you want your business plan to accomplish.
THE BEST TIPS WHEN PRESENTING YOUR BUSINESS PLAN
- Know the outline thoroughly so it is easy for the audience to understand your business case.
- Provide practical examples of the things you have achieved so far.
- Rehearse the presentation
- Be familiar with any equipment to avoid connection or presentation issues.
- Learn how to create stakeholder interest in your business plan by having some topics to be discussed and voted on.
FINAL TIPS FOR YOUR BUSINESS PLAN
- Your business plan needs to be kept up to date.
- You need to put some thought into it to start with, and when changes occur, you need to update it to stay on track.
- Ask your business partner to be a part of the process. Everyone involved in the business should have a say in its future direction.
- Use your accountant’s knowledge and services. A good accountant can assist you in preparing a good business plan.
- Get top professional business strategy support. We run business strategy workshops and consulting sessions. Contact us.
Next > Secure a copy of this business plan template today!
CONCLUSION
Having the best business plan by using a professionally designed template is an important tool for business owners, CEOs, managers and entrepreneurs.
A well-crafted business plan provides structure and guidance for strategic planning, goal setting, financial management, and marketing. Whether you’re starting a new business, seeking funding, or planning for business growth, a well-designed business plan is an essential element of your business success.
eDigital can help you conceptualise, plan, develop, run and optimise successful digital marketing campaigns that generate leads and sales for your brand.
Our digital marketing services include:
- Strategic planning for social media and other digital marketing channels.
- Online advertising management and optimisation: Google Ads Search, Display, Re-marketing and social media advertising.
- Training: social media marketing training and digital marketing training.
- SEO strategy and execution. Including content development:articles, stories, eye-catching and SEO-optimised visuals.
- Celebrity and influencer marketing campaign strategy.
- Brand development. Logo creation, brand personality development and design of marketing materials.
- Consumer contests/competitions/giveaways.
- Email marketing. Dip sequence design and deployment.
- Conversion rate optimisation. It is also called “path to purchase” optimisation.
Contact us today and start boosting your leads and sales.
Hundreds of marketers have supported us with their generous donations. Please donate today! or join 5k+ marketers receiving our e-newsletter.
Final note: Want to reduce customer acquisition costs and dependency on paid media? eDigital‘s marketing strategy training will unmercifully review your marketing, help you build a marketing engine with channels and assets you own, stir your team’s thinking, bring new ideas for new conversion paths and boost customer lifetime value.
THE BEST BUSINESS PLAN TEMPLATE
Mau is one of the most popular marketing consultants offering the best marketing strategy training and the best social media training. Top marketers use Mau’s popular Digital Marketing Plan and Social Media Plan templates
Book Mau for your next training day or join 5k+ marketers receiving Mau‘s e-newslette