Support us 😍
Our mission: To provide marketers with free content while we avoid getting real jobs.
Your impact: Your support pays for our content manager’s existential crisis each morning as she frantically updates this article so you can get these “insights” without paying a dime.
The honest truth: Without your donation, we might have to face the prospect of putting up a paywall like every other content site on earth.
Donate now because we’ve already maxed out our crappy bank’s credit limit and we ethically don’t want to open an OnlyFans account featuring our “questionable” attractive bodies.
But hey, don’t just donate 10 bucks! that barely covers our content manager’s neurological side effects after updating 92846 articles in the last year.
😉
THE TOP 19 ETHICAL ISSUES IN MARKETING
The top 19 ethical issues & challenges in marketing. The marketing ethics affecting consumers & examples. Ethical marketing and how it affects consumer behaviour and spending.
Written by Mau, Global Head of Marketing Strategy at eDigital.
THE TOP 19 ETHICAL ISSUES IN MARKETING
Some of the world’s top marketing executives and business leaders are implementing ethical marketing policies to guide their communication, pricing, advertising, research and competitive strategies.
For example, when consumers purchase from a business, their expectations include wanting to be treated fairly by the sales teams and customer service reps and paying a fair price for the quality of the product/service.
Ethical marketing decisions and efforts should meet and suit the needs of customers, suppliers and business partners.
Recent global consumer preferences and trends show that consumers prefer ethical companies. As a result, marketing ethics are a selling point and a component of a well-established corporate image.
However ethical problems and challenges in marketing start from conflicts and disagreements and unethical behaviour such as price wars, selective advertising, unfair refund policies and deceptive marketing can negatively impact a company’s relationships with its customers.
Each party in a business transaction brings a set of expectations regarding how the business relationship and transaction should exist and be conducted. Each facet of marketing has ethical danger points as discussed below.
THE TOP 19 MOST COMMON ETHICAL CHALLENGES IN MARKETING
19. Exploiting consumers’ patriotism
Using patriotic elements like the new American flag in marketing is generally an ethical issue and it can become a serious ethical problem when it involves deception, manipulation, or disrespect. The distinction lies in intent, execution and impact.
There have been notable instances where brands have used national flags in ways that many consider unethical, often to exploit consumer patriotism for commercial gain.

Puma cat logo gold suede sneaker new American flag.
This highlight the fine line between patriotic marketing and cultural insensitivity or exploitation.
Marketers can cross ethical boundaries when using patriotic symbols like the American flag. While such national patriotic symbols can evoke strong national pride, their use in marketing must be handled with sensitivity and respect to avoid perceptions of exploitation.
Note: Sometimes marketers take advantage of consumers’ patriotism to distract them from other unethical marketing practices (e.g., selling defective products under the guise of “American-made pride”), that involves clear ethical conflict.

Ralph Lauren’s Polo new American flag sweater.
18. Virtue Signalling
Virtue signalling in marketing is when a brand publicly expresses support for a social cause or value (e.g. sustainability, equality, mental health) mainly to enhance its image, without backing it up with meaningful action.
Examples of virtue signalling in marketing:
- Posting slogans like “We stand with women” or “We care about the planet”, but having no internal policies or action plans related to those causes or a supply chain or leadership structure that contradicts those values.
- Adding a rainbow logo during Pride Month, yet failing to support LGBTQ+ employees or causes at any other time.
- Launching campaigns tied to mental health awareness, but providing no real resources, donations, or organizational changes.
The top 3 reasons why virtue signalling is an ethical marketing issue:
- Erodes consumer trust once audiences see the disconnect between messaging and reality.
- Invites public scrutiny and social media backlash.
- Undermines genuine efforts made by activists or organisations
- Damage brand reputation, especially with Gen Z and Millennials who value transparency and action.
How to Avoid Virtue Signalling in your marketing:
- Back your message with action: If you support a cause, show how — through policies, donations, partnerships, or measurable outcomes.
- Be transparent: Acknowledge where you’re making progress and where there’s work to do.
- Involve stakeholders: Work with the communities you’re representing, not just speaking about them.
- Make your values part of your operations, not just your marketing.
Marketers are using this best social media policy (guidelines) template
17. Tokenism
Tokenism in marketing refers to the superficial or symbolic inclusion of underrepresented or marginalised groups (such as women, racial minorities, LGBTQ+ individuals, or people with disabilities) in campaigns without meaningful engagement, representation, or action behind it.
You know your marketing is being treated as tokenism when you are using diversity just as a checkbox: Featuring a person of colour, a woman, or someone with a disability in an ad just to appear inclusive, without giving them a real voice or relevance to the story.
Your marketing can also be seen as tokenism when you highlight a social issue only during a trend or holiday (e.g. posting about International Women’s Day or Pride Month, but doing nothing to support those communities year-round).
When you promote inclusivity externally while internal practices don’t reflect it is also a form of tokenism. For example, celebrating women’s achievements in ads while having no women in leadership internally.
Tokenism also refers to surface-level representation: Using diverse visuals or language but failing to address the deeper challenges those groups face or benefit them meaningfully.
Tokenism is an ethical issue and a problem in marketing because it lacks authenticity and can come across as insincere or exploitative. Tokenism damages brand trust, especially if consumers or employees expose inconsistencies.
Tokenism invites consumer backlash on social media as audiences demand accountability and you are not actually producing real impact.
How to avoid tokenism in your marketing:
- Hire diverse voices behind the scenes — not just in front of the camera.
- Involve communities in creating the message and ensure it reflects their lived experiences.
- Commit to real change; for example, support initiatives, invest in education, ensure representation in leadership.
- Be transparent about your intentions and actions.
An example of tokenism: A brand posts a black square on social media during Black Lives Matter protests, but has no Black leadership or diversity policies.
What’s the opposite of tokenism? A brand’s marketing that is authentic, accountable and that is producing real change.
For example, a brand post a black square on social media during Black Lives Matter protests – supporting the movement – but also funds scholarships for Black students, partners with Black creators and publishes a racial equity audit.
A real example of tokenism in marketing was Pepsi’s Kendall Jenner Ad (2017). Pepsi’s ad featured Kendall Jenner was widely criticised for trivialising serious social justice movements. The ad showed Jenner joining a protest and resolving tensions by offering a police officer a can of a drink with the new Pepsi logo, which many perceived as an attempt to capitalise on activism for commercial gain. The backlash led Pepsi’s marketing team to pull the ad and issue an apology.

Tokenism an ethical issue in marketing – Kendall Jenner featured in an ad offering a can with the new Pepsi logo.
16. Marketing “true crime” entertainment
The rising popularity of murder-focused books, podcasts and YouTube channels has sparked an ongoing conversation about the ethics of “True Crime” entertainment.
Some people are concerned about sensationalism and exploitation when marketing “True crime” novels, series and stories.
Should “True Crime” writers, creators and publishers also prioritise healing and restoration by giving back to survivors a portion of the money they earn by telling their stories?
The solution: consider emphasising alternative reading options that offer more positive or uplifting content and/or stories. If you sell books, you can offer incentives for exploration, for example: incentivise people to opt for books that enrich their lives in positive ways.
Popular this month: the top reasons why good people do bad things
15. Social media mocks of celebrities’ mess-ups
Mocking celebrities’ mistakes by publishing nasty comments on social media has become a way for some marketers to get the public’s attention.
Some argue that celebrities should not be ridiculed on social media as they can be already severely devastated and/or emotionally affected because of their mistakes and should be treated with privacy and respect.
While on the other side, some people may argue that they love these brands that mock celebrities because they simply do not give a f*ck.
Would this tactic be effective for building a positive brand reputation in the long term?
Tell us your opinion.

social media strategy celebrity funny meme
Some of the brands we have seen using the “Mock celebrities” tactic include Ryanair and others.
The solution: When discussing a prominent celebrity or industry leader, ensure that your contribution to the conversation is constructive and respectful. Avoid ridiculing individuals based on their mistakes, appearance, gender, age or ethnicity.
Trending this week: the world’s top 25 most popular people on TikTok
14. Greenwashing
Greenwashing is when marketers overrepresent the extent to which their brands and their material sourcing, manufacture, delivery and marketing are environmentally friendly, sustainable or ethical.
For example, the potential to mislead can arise as a result of a business being unclear on what standards they use to assess the product as environmentally or socially responsible; or overstating green credentials that are not sufficiently reflected in their operations and practices.
This misrepresentation distorts relevant information that a current or prospective customer might require to make an informed buying decision.
The solution: you can take this “Green Marketing Challenge” developed by the United Nations and check how well you can identify which green claims are more likely to promote sustainability and empower sustainable consumption decisions.
Marketers are using some of the best 25 sustainability hashtags on TikTok
13. Museum marketing: marketing of stolen goods
“Return what was stolen from us”
That’s the demand from indigenous cultures to some of the world’s top museums.
As most museums are funded by the Government( basically taxpayers’ money), is it ethical for marketers working for museums to spend money marketing the binge-watching of stolen goods?

Museum marketing of stolen goods ethical considerations National Geographic post on Facebook.
The solution: Inquire with your local museums about the provenance of their exhibited artifacts. If they are unable to provide a satisfactory answer, there is a possibility that the items may have been unlawfully acquired from other indigenous or ancestral communities.
Marketers are accessing the exclusive list of top 250 most popular Australians on Instagram.
12. Child exploitation in advertising
The average parent may not be savvy or careful enough to protect their kids from model and talent agencies offering them quick cash to let their kids be part of creepy ad campaigns. You – the marketer – have to step in and ensure any image that uses minors’ talent is fully checked and approved by your marketing and legal teams before launching/publishing it.
Children of all ages must be the most protected humans from pervasive advertising and marketing practices.
The solution: Prior to launching a marketing campaign involving children, consult both your marketing and legal teams to determine if showcasing photos of children, particularly in association with controversial themes, is necessary or appropriate.
Note: Manipulation of children can be also seen in the gender marketing of children’s toys and clothes. While gender equality and expectations are evolving rapidly, some old-fashion marketers still think little girls only want Barbie dolls in pretty, pink dresses and little boys just want big, blue trucks. Gendered children’s toys/clothes marketing is a real issue for brands all over the world and its impact on children’s development has been widely documented.

Balenciaga scandal ad campaign child bdsm bondage toy controversial kid photos
Editor’s pick: the most popular emojis teens are using this year
11. Marketing incomplete or defective products
Would you pay a premium price for a meal in a fine dining restaurant that does not offer you a clean table and cutlery so you can comfortably enjoy your celebrity chef’s culinary dish?
A similar situation is happening with already high-priced iPhones. Claiming “environmental” benefits, iPhones no longer come with a charger and earphones. The Brazilian government banned Apple from selling iPhones without a battery charger in Sep 2022, claiming that the company provides an incomplete product to consumers.
The solution: Ensure that the product or service you offer can be fully utilised and enjoyed by your customers.
Other examples of incomplete or defective products include:
- Samsung Galaxy Note 7 (2016). Samsung’s Galaxy Note 7 was marketed as a cutting-edge smartphone with advanced features. However, the device was prone to overheating and catching fire due to battery defects. The company issued a recall, but replacement units also experienced similar issues. This led to a global recall of 2.5 million devices and a loss of approximately $17 billion.
- Volkswagen Diesel Emissions Scandal (2015). Volkswagen marketed its diesel vehicles as environmentally friendly, boasting low emissions and fuel efficiency. However, it was revealed that the company had installed software in the cars that manipulated emissions tests, allowing them to pass while emitting pollutants far above legal limits during regular driving. This scandal affected around 11 million vehicles worldwide and led to significant legal and financial repercussions for the company.
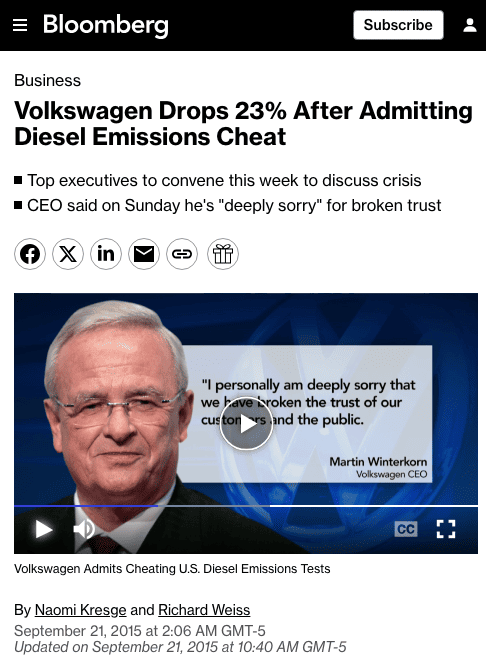
cheating on product features an ethical issue in marketing – Bloomberg.
Marketers are learning how to write the best customer service plan and template
10. Unethical market research
Some ethical problems in market research are the invasion of privacy and stereotyping.
The latter occurs because any analysis of real populations needs to make approximations and place individuals into groups. However, if conducted irresponsibly, stereotyping can lead to a variety of ethically undesirable results.
The solution: Limit the collection of personal details from participants in your market research to maintain their anonymity. Additionally, when presenting insights and results from market research, be sure to include the diversity of responses from your sample, not just the similarities.
Marketers are also reading the world’s top 10 market research companies
Join 5k+ marketers receiving the best marketing tips.
9. Unethical customer segmentation
Selective marketing is used to discourage demand from so-called undesirable market sectors or disenfranchise them altogether.
Some of the most popular unethical market audience exclusion are biased attitudes towards gay, religious or ethnic minorities, people with disabilities and/or plus-size body markets.
In the screenshot below, an event organiser in Australia is assuming black/brown ppl may not be able to afford to pay the full price of a ticket for an event.
This can be seen as very rude not only by dark skin colour people but also by white skin colour people who are in economic hardship as they may feel left out of these types of discounts.
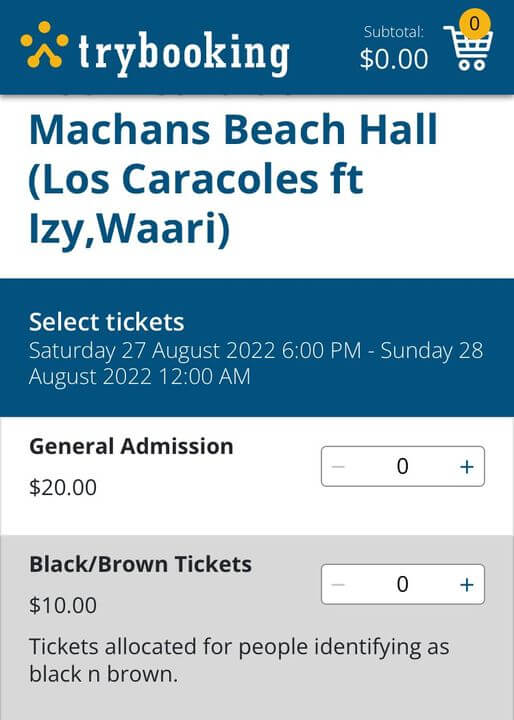
Marketing ethics racism event ticket white supremacy Machans Beach Cairns Australia
Another ethical issue relates to uneducated vulnerable audiences in emerging markets/developing countries, as the public there may not be sufficiently aware of skilled marketing ploys, dirty schemes and scams.
The solution: Allocate resources towards educating your team, partners, and customers about your products and services, as well as potential scams. Implement and enforce policies to prevent discrimination against vulnerable minorities or disadvantaged ethnic communities.

The Nike brand embraces cultural diversity in its marketing and advertising – “Believe in something even if it means sacrificing everything” Nike ad Colin Kaepernick American football player 2018 – Marketer of the Year by Adage
Marketers are using the best Strategic Marketing Plan – template.
8. False or exaggerated remarks about a brand
In the 1940s and 1950s, tobacco used to be advertised as promoting health. Today, an advertiser who does not tell the truth, may offend consumers and break the law. However, the law permits puffery (a legal term). The difference between mere puffery and fraud is a slippery slope.
What is puffery?
Puffery refers to exaggerated or false praise. Puffery serves to “puff up” what is being described. In law, puffery is usually invoked as a defence argument: it identifies futile speech, typically of a seller, which does not give rise to legal liability.
The solution: The best way to avoid exaggerated remarks about your brand, product or service in marketing communications is to focus on providing accurate verifiable facts, truthful evidence and meaningful information about your products or services.
7. Erotic, religious and violent themes
Erotic suggestions in marketing campaigns and/or advertisements may be regarded as a form of harassment.
The Adidas contentious and viral ad featuring Addison Rae’s“Father son Holy Spirit” bikini inspired other popular celebrities to wear the controversial bikini such as Victoria de Angelis a popular Italian bassist of the rock band Måneskin.
The team behind the promotion of Victoria de Angelis and her rock band know how to sell music online and may have crafted a social media strategy that creates controversial viral content to earn the attention of prospective music fans who connect with rebellious themes.
The advertising of certain products may strongly offend some people while being of interest to others.
Examples include feminine hygiene products as well as hemorrhoid and constipation medication.
The advertising of condoms has become acceptable in the interests of AIDS prevention but is nevertheless seen by some religious groups as promoting promiscuity.
Violence themes in marketing or advertising are a massive issue, especially when used in children’s advertising and/or advertising likely to be seen by kids.
In 2015, the UK’s Advertising Standards Authority banned a double-page Miu Miu ad with actor Mia Goth (then 22) that ran in British Vogue.
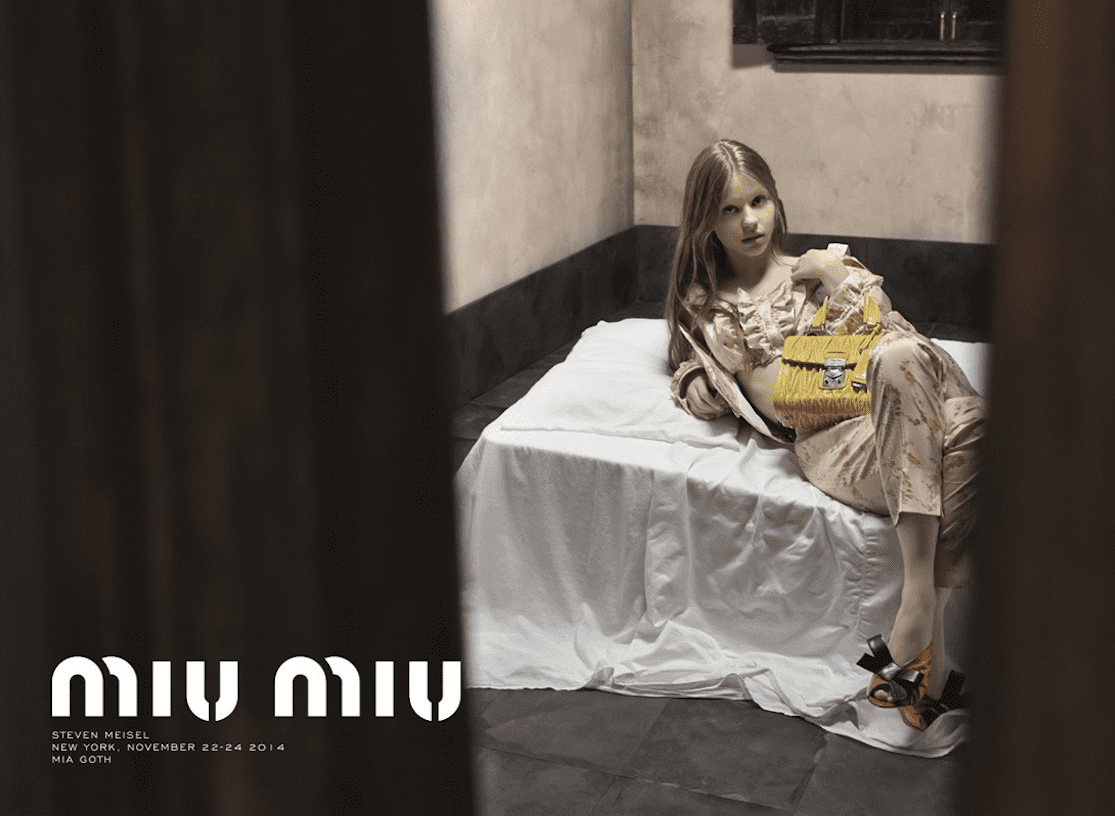

Miu Miu banned ad Mia Goth 2015. Miu Miu is one of the world’s top 25 most-followed luxury brands on Instagram.
The solution: You should understand the demographics and preferences of your target audience to ensure that your advertising aligns with their values and beliefs. You can emphasise positive and uplifting messages in your advertising campaigns rather than relying on controversial or provocative themes. You can also select imagery that is neutral and non-controversial to avoid inadvertently conveying messages related these controversial themes.
Be mindful of cultural sensitivities and taboos when creating advertising content for diverse audiences.
You can conduct research or seek feedback from cultural experts to ensure that your marketing and/or advertising messaging is respectful and appropriate.
Only in comedy, using these themes can be a great strategy.
Some of the top 25 Australian Comedians are well-known for using controversial themes to bring laugh to their audiences and fans.
6. Marketing products made at exploitative factories
Look no further than the Dyson brand, which recently found itself toppled from its position as an innovation darling to being cast as an ethical villain following claims that the company was outsourcing to a supplier that allowed poor working conditions and exploitative practices in its Malaysian factories.
Dyson immediately terminated its contract, but not before the supplier, ATA IMS, had lost two-thirds of its value.
The solution: conduct due diligence which means research and vet potential suppliers to ensure they adhere to ethical labor practices. Look for certifications such as Fair Trade or ethical sourcing initiatives. Whenever possible, visit factories and production facilities to assess working conditions firsthand and ensure compliance with labor laws and ethical standards.
Join 5k+ marketers receiving the best marketing tips.
Employees and factory workers that have been exploited in some form or shape by their employers are using protest art to vocalise their struggles.
You are about to discover some of the world’s top 10 most popular protest art.
5. Negative advertising techniques
Through negative advertising techniques, the advertiser highlights the disadvantages or creating rumours of its main competitor rather than the advantages of their own brand.
These methods are especially used in politics and also seen in other industries.
One of the world’s most popular negative advertising examples was when Microsoft launched the “Scroogled” campaign to criticise Google’s shift to a pay-per-click model for Google Shopping and its use of user data for targeted advertising.
The “Scroogled” campaign featured ads that mocked Google’s practices, such as a video where a person asks Google about “walled gardens” and receives irrelevant search results.
While the campaign garnered attention, it also drew criticism for being overly aggressive and potentially misleading.
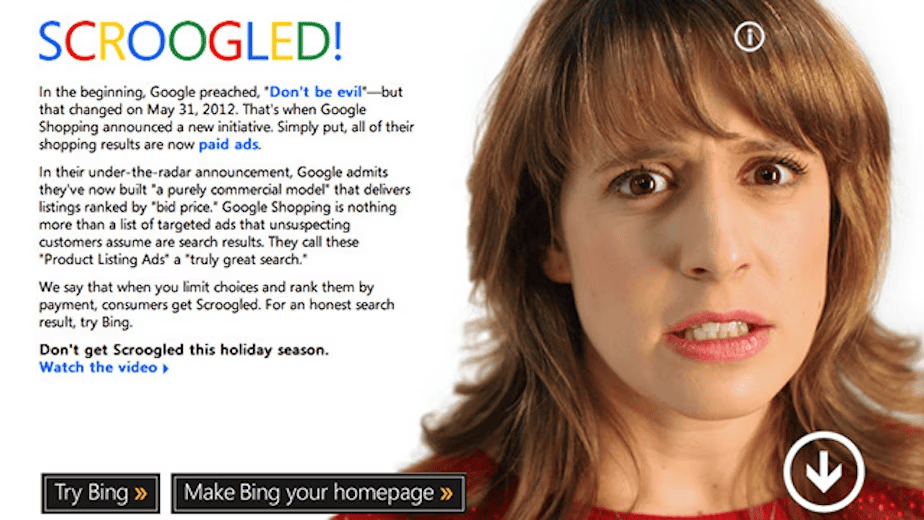
negative advertising an ethical issue in marketing
The solution: To create ethical ads and promotions, train your teams to focus on finding valid solutions for their prospects, even if it means not making a sale or even if it means recommending a competing product. There’s little worse than destroying your brand’s reputation by pushing a product that doesn’t fit the end user’s needs or desires.
Marketers are using the best Influencer Marketing Brief – template.
4. Unsolicited marketing communications
Direct marketing is the most controversial of advertising channels, particularly when approaches are unsolicited.
Yes, I know what you are thinking: those annoying flyers and catalogues filling up your mailbox.
TV commercials, pop-up banner ads and direct mail are common examples. Email spam and telemarketing push the borders of bad marketing practices and legality more strongly.
The solution: Ensure transparency by informing potential customers about the source of their email or phone numbers and provide a clear option for unsubscribing from future messages.
Marketers are using some of the top 25 most popular hashtags on TikTok.
3. Misleading marketing communications
Deceptive marketing is not specific to one target market, and can sometimes go unnoticed by the public.
There are several ways in which deceptive marketing can be presented to consumers; one of these methods is accomplished through the use of humour.
Humour provides an escape or relief from some kind of human constraint, and some advertisers take advantage of this by deceptively advertising a product that can potentially alleviate that constraint through humour.
A real example of misleading marketing was Red Bull’s “Gives You Wings” Campaign. The Red Bull’s slogan, “Red Bull gives you wings” was widely recognised and associated with the brand’s image of providing energy and enhancing performance. However, in 2014, the company faced legal action over allegations that the slogan was misleading. A class-action lawsuit claimed that Red Bull’s marketing suggested the drink offered benefits like improved physical performance and faster reaction times without scientific evidence to support these claims. The lawsuit argued that the slogan and advertising misrepresented the product’s effects on consumers.

misleading advertising an ethical issue in marketing – Reb Bull “gives you wiiings” ad campaign featuring the new Red Bull logo.
In response, Red Bull agreed to settle the lawsuit for $13 million, without admitting wrongdoing. The settlement provided refunds to consumers who had purchased Red Bull products between 2002 and 2014, and the company also agreed to modify its advertising practices.
This popular Red Bull’s “Give You Wings” slogan highlighted the potential legal and reputational risks associated with exaggerated, literal interpretations or unsubstantiated advertising claims.
As a result, Red Bull’s just changed the tagline/slogan to: “Give You Wiiings” (three iii’s) making it look more as a metaphor that should not be taken literally.
Genius? Probably. Ethical? Probably not.
How to avoid misleading consumers:
- Ensure that your advertising claims are truthful and substantiated, even when using humour or exaggeration. While creative and humorous campaigns can be effective, they must not mislead consumers or make unverified claims about a product’s capabilities.
- Communicate honestly and transparently with your audience, just as you would expect to be treated. Focus on addressing their needs rather than resorting to deception. If your product aligns with their needs, sales will naturally follow. If not, be willing to adapt your product or persuade your audience to reconsider their preferences.
Most shared this month: Australia’s worst misleading advertising examples
2. Anti-Competitive practices
2.1. Bait and switch
Bait and switch is a form of fraud where customers are “baited” by advertising for a product or service at a low price; a second later, the customers discover that the advertised product – with the awesome price – is not available and are “switched” to a costlier produ.ct.
The solution: Establish a protocol to regularly verify the availability of advertised products. Implement automated alerts for your marketing team, agencies, and publishing partners to promptly identify when popular products become unavailable.
2.2. Planned obsolescence
Planned obsolescence is a policy of designing a product with a limited useful life, so it will become unfashionable or no longer functional after a certain period of time and put the consumer under pressure to purchase again.
Apple is known for making their iPhones harder to update to the latest technologies. For example, millions of people are still using the iPhone 6 and iPhone 7 but it has become impossible to update to the latest IOS software.
The solution: Maintain comprehensive records of all communications to ensure customers are informed about the product life cycle, including the expected optimal performance duration of your brand.
2.3. Pyramid schemes
A pyramid scheme is a non-sustainable business model that involves promising participants payment or services, primarily for enrolling other people into the scheme, rather than supplying any real investment or sale of products or services to the public.
A pyramid scheme relies on getting the initial investor or “captain” to enrol others for a fee to them who in turn will also enrol others in order to get paid.
Note: Affiliate programs that reward your customers for bringing new customers to your business is a legit marketing activity.
The solution: Keep your team and customers informed about emerging unethical and harmful pyramid schemes in your industry and emphasise the importance of never participating in or promoting such schemes or programs.
Marketers checked out this year’s top 10 social media marketing trends.
1. Unethical pricing
There are quite a few unethical pricing strategies some companies use to boost sales and gain market share.
1.1 Bid-rigging (also known as collusive tendering)
Bid-rigging, also referred to as collusive tendering, occurs when two or more competitors agree they will not compete genuinely with each other for tenders, allowing one of the cartel members to ‘win’ the tender. Participants in a bid-rigging cartel may take turns to be the ‘winner’ by agreeing about the way they submit tenders, including some competitors agreeing not to tender.
The solution: When competing for tenders, allow your competitors to submit their bids, maintain transparency, and refrain from engaging in price-fixing activities. If you’re issuing a contract, monitor for any indications that top suppliers are not participating in the tender process, and inquire about any reasons why they may have chosen not to bid.
1.2 Predatory pricing
With well-managed economies of scale and optimal supply chains, you may be able to offer a price no one can offer. However, predatory pricing is the practice of selling a product or service at a low price, with only the intention to drive competitors out of the market or create barriers to entry for potential new competitors.
Numerous articles available online have highlighted the predatory pricing strategies and practices employed by the e-commerce behemoth: Amazon.
The solution: Make sure your business can justify competitive pricing for its products or services in the market. It’s advisable to demonstrate (if necessary) the operational efficiencies that enable your company to offer such competitive prices.
Pricing is a key component of a well-crafted business plan.
Marketers are using this best business plan template.
Marketing ethics – meaning
Marketing ethics, regardless of the product offered or the market targeted, sets the guidelines for which good marketing is practised.
Marketing ethics and social responsibility
To market ethically and effectively one should be reminded that all marketing decisions and efforts are necessary to meet and suit the needs of customers, suppliers, and business partners.
The mindset of many companies is that they are concerned for the population and the environment in which they do business. They feel that they have a social responsibility to people, places and things in their sphere of influence.
Role of ethics in marketing
Using ethics as a marketing tactic
Large companies fear the damage to their image associated with press revelations of unethical marketing practices.
Marketers have been quick to perceive the market’s preference for ethical companies, often moving faster to take advantage of this shift in consumer preference for ethical companies.
This results in the propagation of ethics itself as a selling point or a component of a corporate image.
Marketers learnt about the top reasons why good people – sometimes – do bad things.
Poor marketing ethics examples
Hairstyles
Is it ethical to tell women they are desirable just because of having straight hair?

black girl curly hair story – The Economist Instagram post
Marketing ethics in consumer behaviour
Other unethical marketing tactics
- Doxxing a popular competitor’s employee or public figure on social media with the objective of shaming, embarrassing, ridiculing or just simply taking competitive advantage.
- Swatting a competitor’s event to make the event a failure.
Key terms
- Doxxing. When the private information of someone gets published with the objective of shaming, embarrassing, ridiculing or taking a competitive advantage.
- Propagation: The dissemination of something to a larger area or greater number.
- Puffery: A legal term that refers to promotional statements and claims that express subjective rather than objective views, which no “reasonable person” would take literally. An example would be “Red Bull gives you wings“.
- Swatting. When someone anonymously calls an emergency number to report a fake emergency that sounds serious enough to elicit a response from a SWAT (special weapons and tactics) team.
Trending this week: the top reasons why good people – sometimes – do bad things
Conclusion
Done right, ethical marketing brings long-term value and loyalty.
There’s a positive correlation between ethical marketing, the quality of consumer/brand relationships, and how consumers perceive product quality; together, they contribute to brand loyalty.
Final note: Are your marketing costs through the roof?
If your customer acquisition costs are climbing faster than a startup founder’s ego (after a successful IPO), and you’re hooked on paid ads like a reality TV star drama or a Tinder date who keeps accepting your dinner invites but never calls you back.
If that sounds like your situation, you should contact us.
Our exclusive digital marketing strategy workshops will mercilessly dissect your marketing, expose all the weak spots, and show you how to ditch the social media algorithms chokehold and build a marketing engine you actually own.
We’ll shake up your team’s thinking, drop fresh ideas and turn your marketing from “meh” to money-making.
Ready to stop burning cash and start making it? Hit us up! We offer:
✔ Digital Marketing Strategy. Because hope is not a plan.
✔ Online Ads (Google, Social, Remarketing). The art of spending money wisely for once.
✔ Social Media Marketing Training. So you stop posting into the void.
✔ SEO Strategy & Execution. Because if Google doesn’t know you exist, do you even?
✔ Influencer & Celebrity Marketing. Get people with clout to talk about you.
✔ Branding & Logo Design. So you don’t look like a dodgy side hustle.
✔ Consumer Giveaways & Competitions. Because people will do anything for free stuff.
✔ Email Marketing & Drip Sequences. Slide into inboxes the right way.
✔ Conversion Rate Optimisation. Turn window shoppers into actual buyers.
Ready to start marketing like a boss? let’s talk. 🚀
THE TOP 19 ETHICAL ISSUES IN MARKETING
Considered one of the best marketing consultants in Sydney (and not just by Mau’s mom), Mau delivers killer digital marketing strategy workshops and best social media training so good, even your grandpa will get it.
5k+ smart marketers who love stealing good ideas receive Mau’s weekly email, while others tired of guessing use Mau’s Digital Marketing Plan and Social Media Plan templates.
Mau is travelling the 🌎 ✈️ probably posting questionable travel choices on TikTok or YouTube